Captive White-Tailed Deer Fawn Mortality Secondary to Strongyloides sp. infection in New York State

By A Mystery Man Writer
Strongyloides sp. has been identified as a cause of high fawn mortality in several New York state captive white-tailed deer (WTD) herds during the last 4 years.
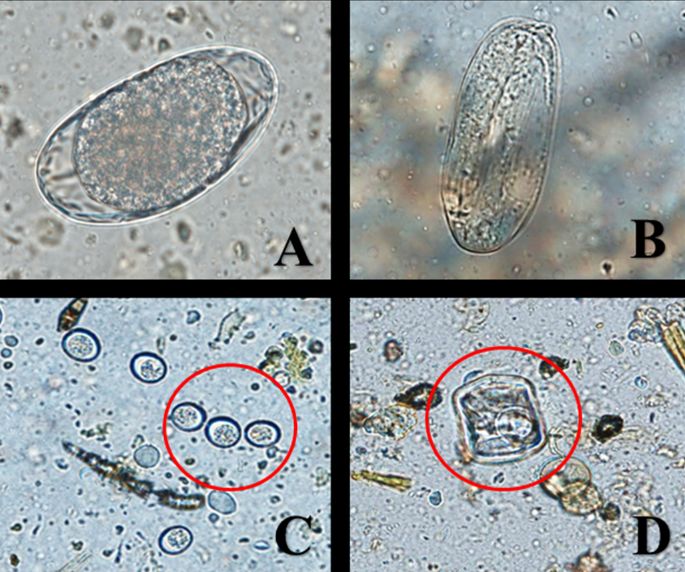
WEC453/UW498: Facts about Wildlife Diseases: Gastrointestinal Parasites of Farmed White-tailed Deer in Florida
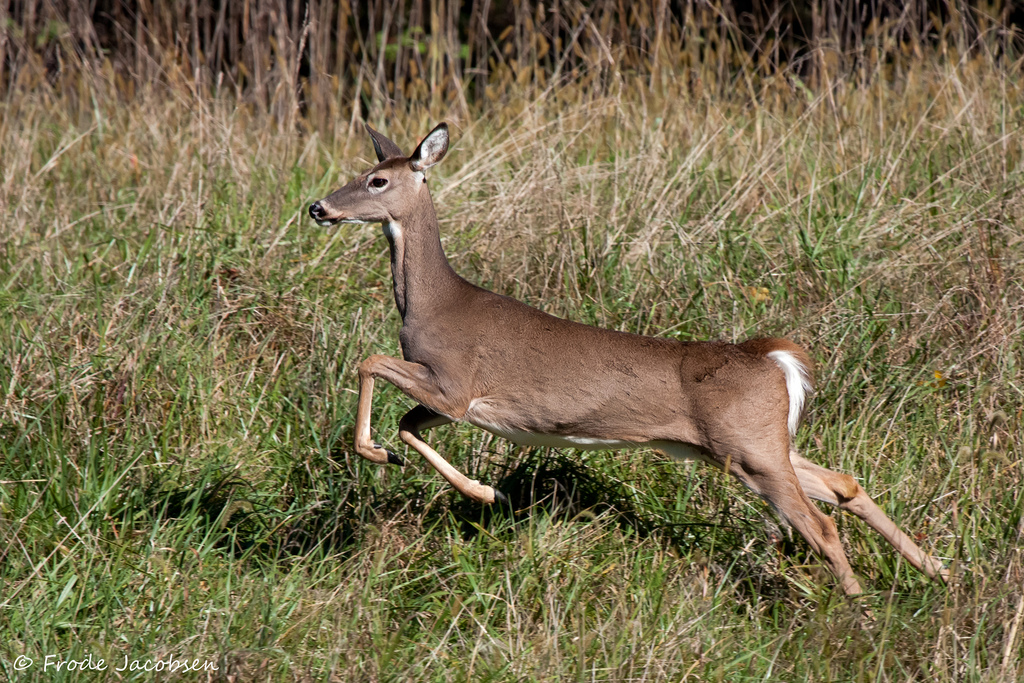

Maryland Biodiversity Project - White-tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus)

Body of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) being decomposed by fly larvae (maggots), eastern carrion beetle (Necrophilia americana), and other Stock Photo - Alamy
Survival of white-tailed deer fawns in central Iowa
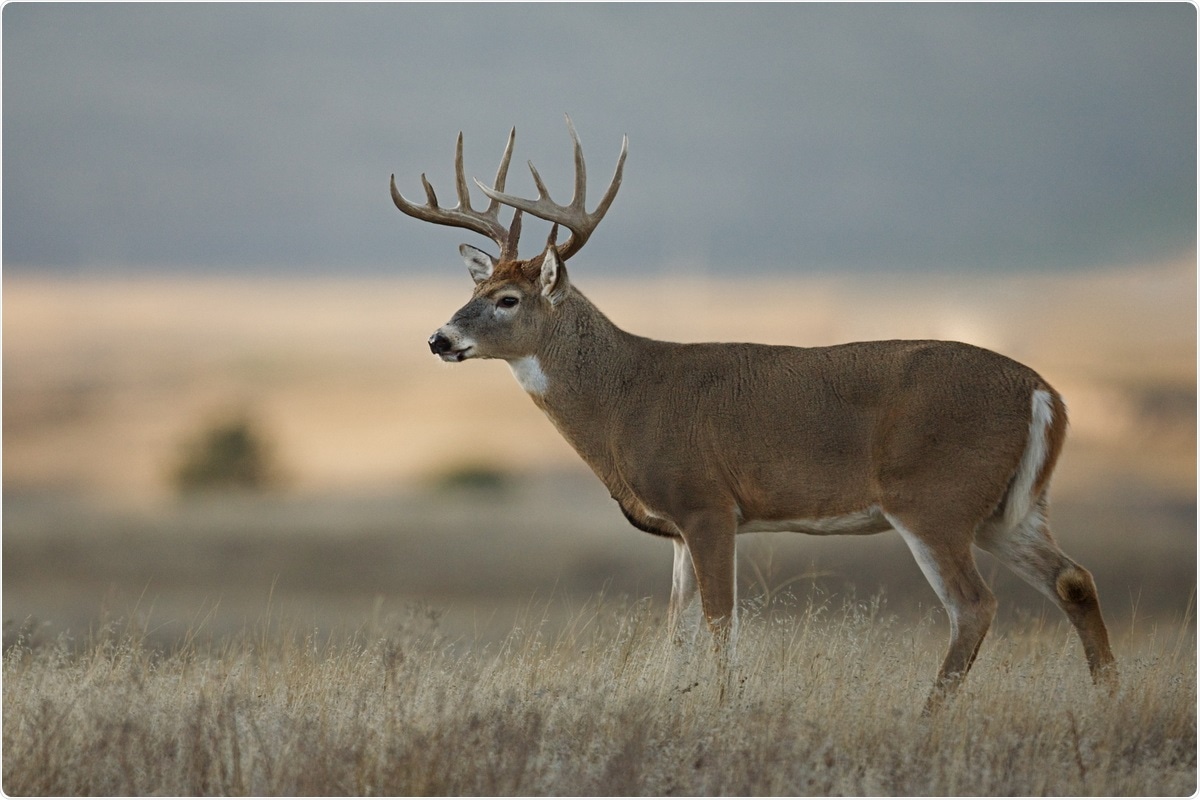

SARS-CoV-2 detected in white-tailed deer with possible zooanthroponotic spillover events

A participatory surveillance of marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) morbidity and mortality in Argentina: first results, BMC Veterinary Research

Pan-American Trypanosoma (Megatrypanum) trinaperronei n. sp. in the white-tailed deer Odocoileus virginianus Zimmermann and its deer ked Lipoptena mazamae Rondani, 1878: morphological, developmental and phylogeographical characterisation

White Tailed Deer - Invasive Species of the Virgin Islands
Survival of white-tailed deer fawns in central Iowa

The prevalence, genetic diversity, and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer in New York

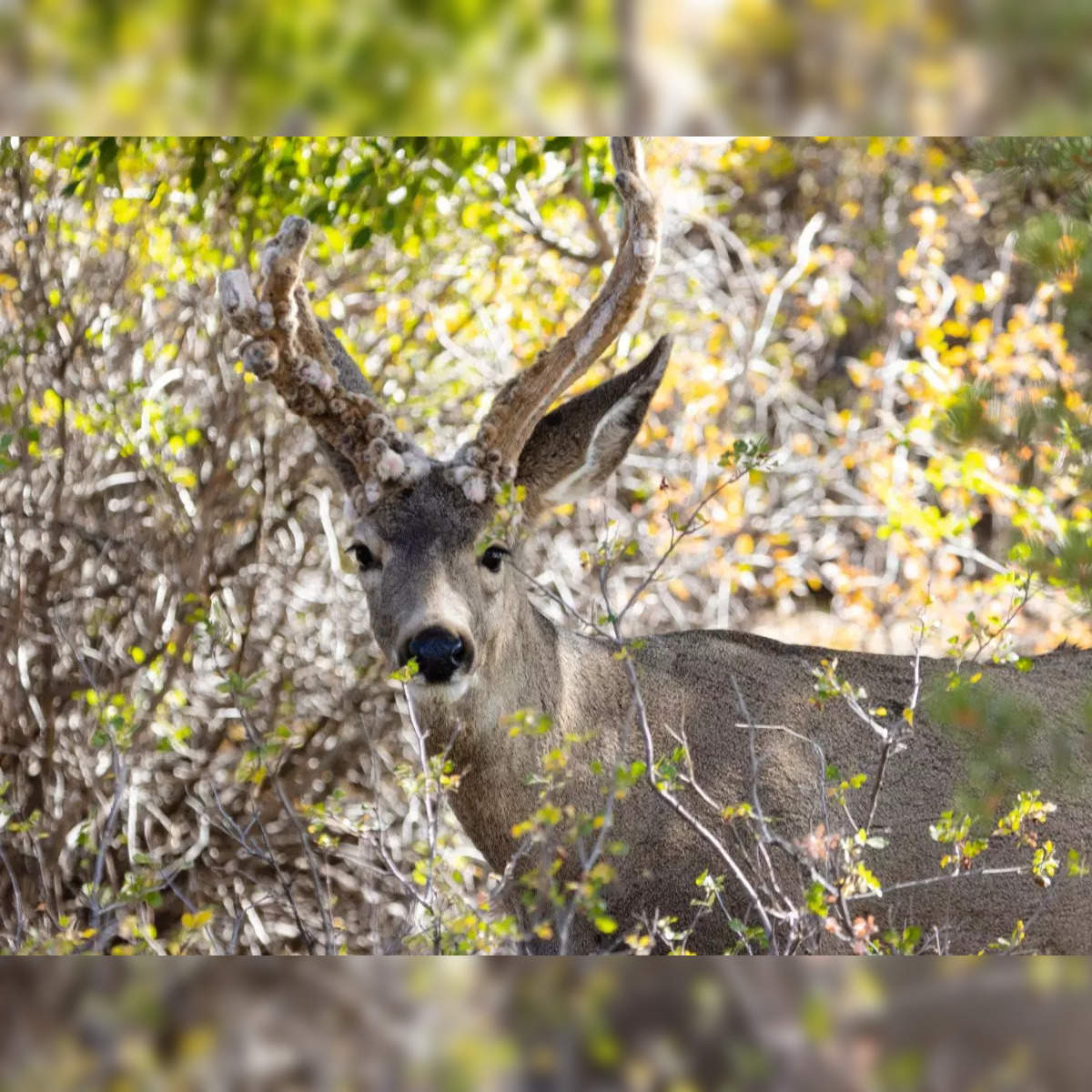
Northeastern deer more susceptible to wasting disease than those to the west
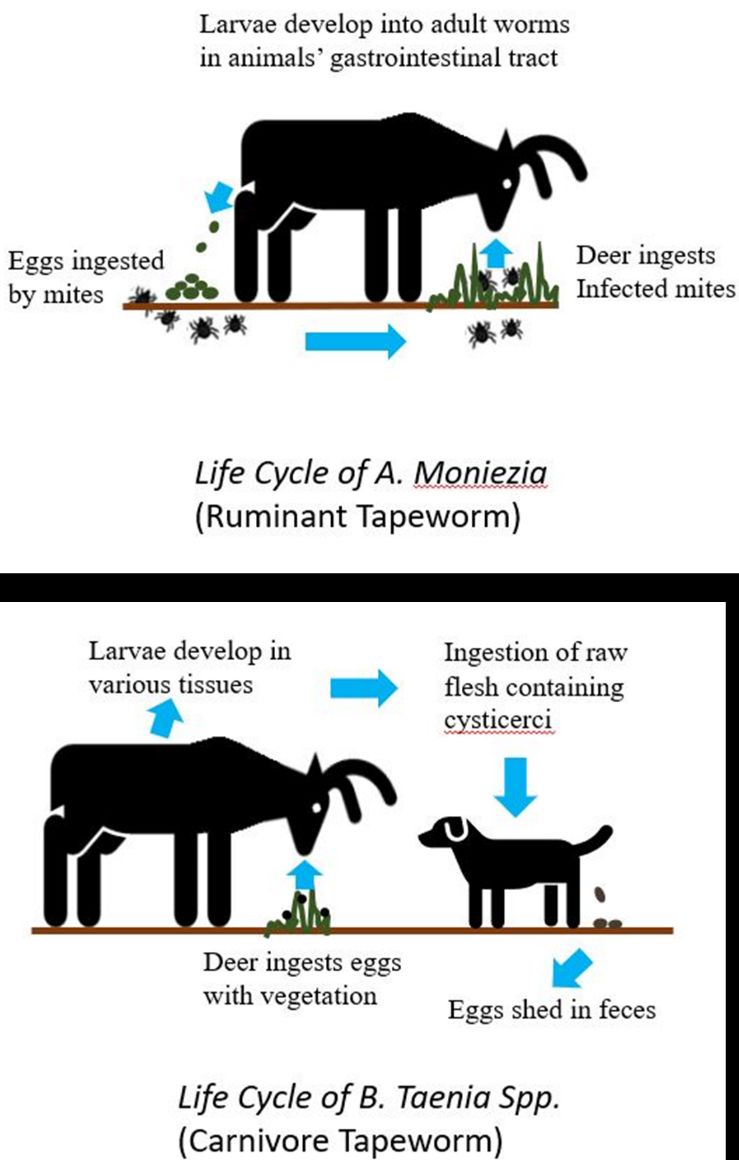
WEC453/UW498: Facts about Wildlife Diseases: Gastrointestinal Parasites of Farmed White-tailed Deer in Florida
- Deer antler base as a traditional Chinese medicine: A review of its traditional uses, chemistry and pharmacology - ScienceDirect

- Ohio deer carry COVID virus: how hunters can protect themselves

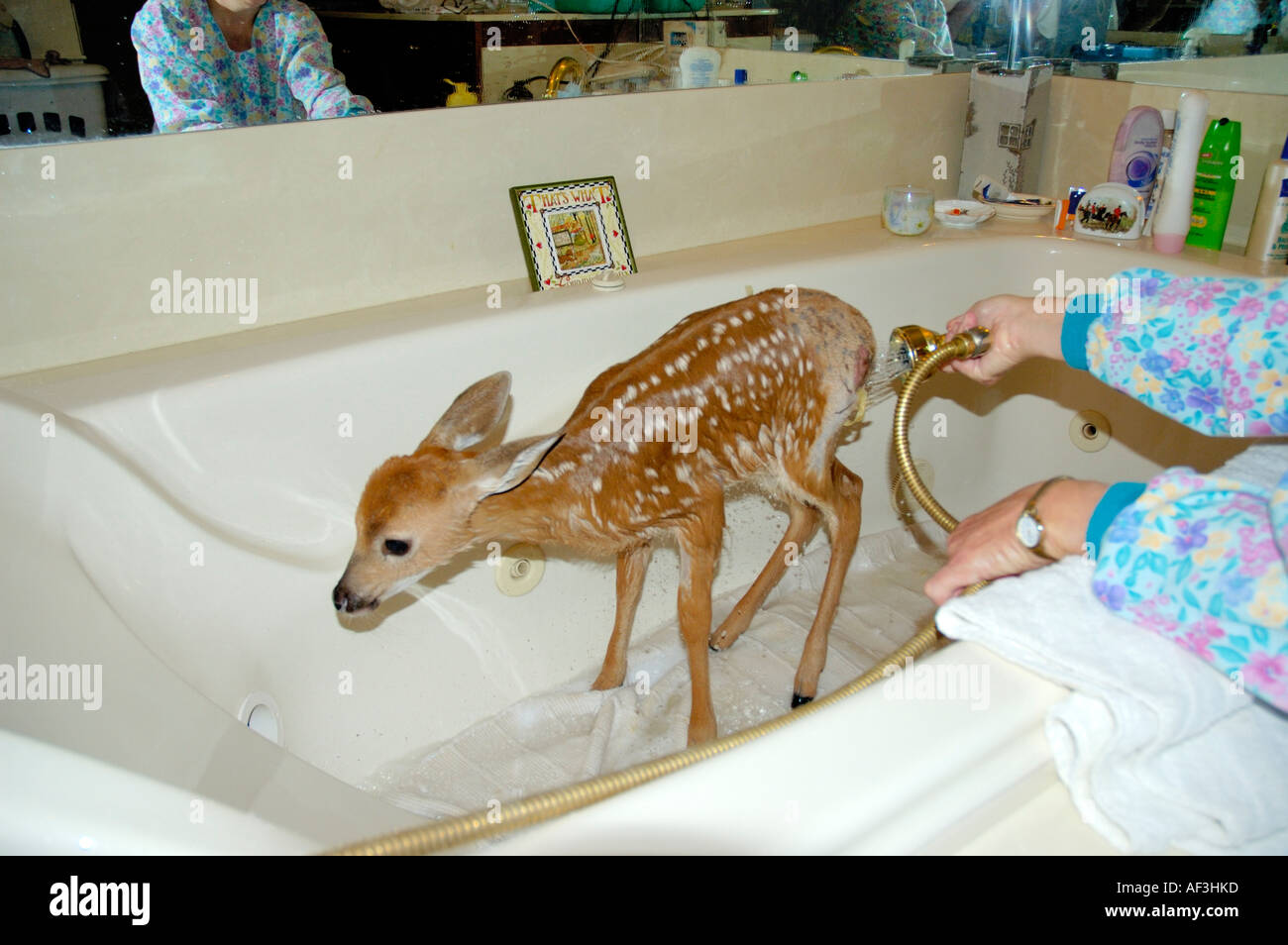
- Young deer fawn being bathed during rehabilitation and medical treatment of injuries Stock Photo - Alamy

- Zombie deer disease' reported in US, Canada, other countries. Check symptoms, treatment, vaccine - The Economic Times

- Deer's antlers – a potent drug - The Linnaean Gardens of Uppsala - Uppsala University, Sweden





