Classical Mechanics - Physics LibreTexts
By A Mystery Man Writer
Classical mechanics describes the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars and galaxies. If the present …
Classical mechanics describes the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars and galaxies. If the present state of an object is known it is possible to predict by the laws of classical mechanics how it will move in the future (determinism) and how it has moved in the past (reversibility)
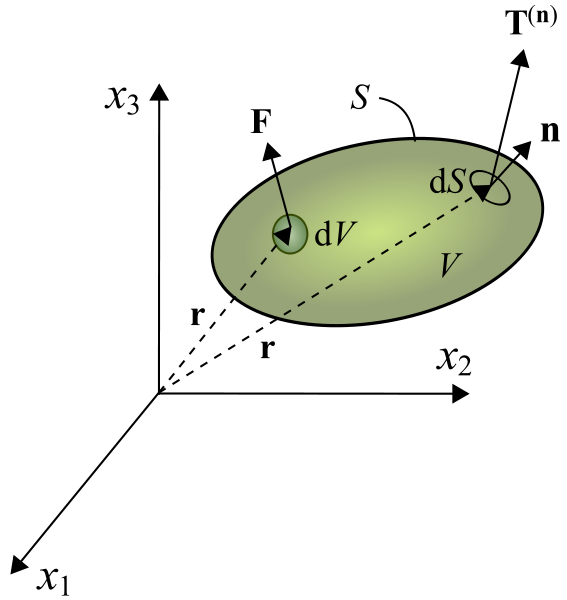
Physics - Classical Mechanics - Rigid Body Equilibrium — Steemit

expectation value quantum mechanics –

Newton's laws of motion, Definition, Examples, & History

9.A Condensed Matter Physics (Answers) - Physics LibreTexts
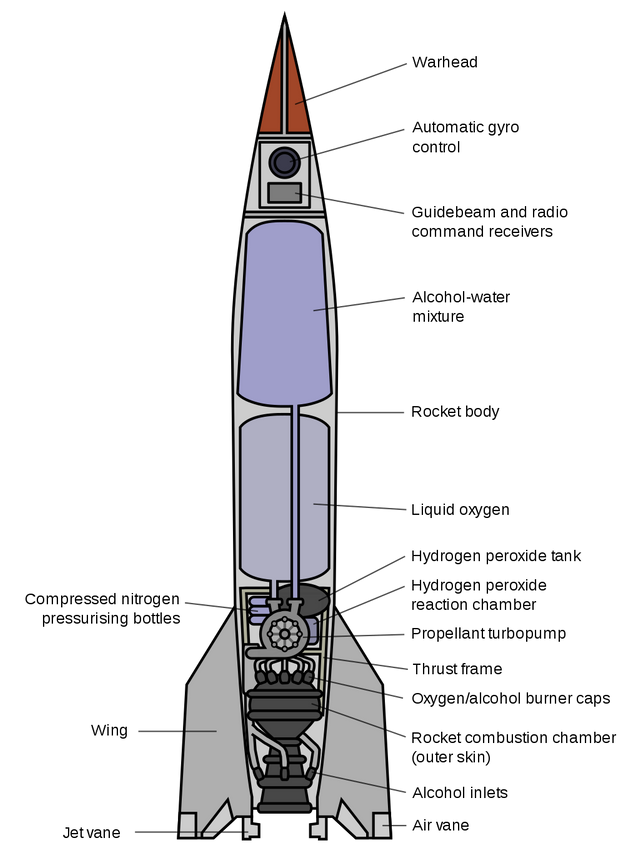
Physics - Classical Mechanics - Explaining the Physics behind Rocket Propulsion — Steemit

1: Introduction to Classical Mechanics - Physics LibreTexts
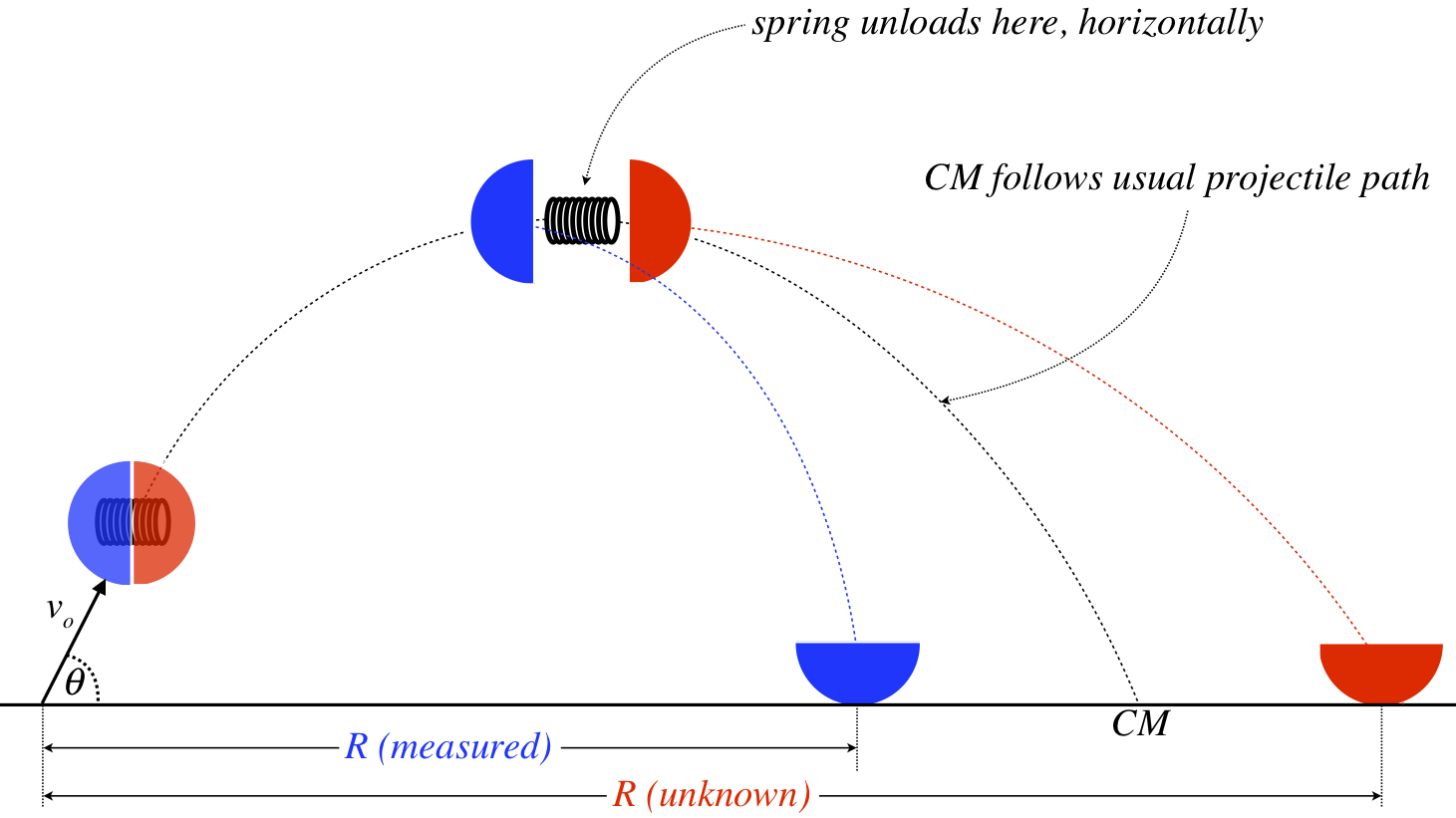
4.3: Momenta of Systems - Physics LibreTexts

1.3 - Units and Standards - Physics LibreTexts PDF, PDF, International System Of Units
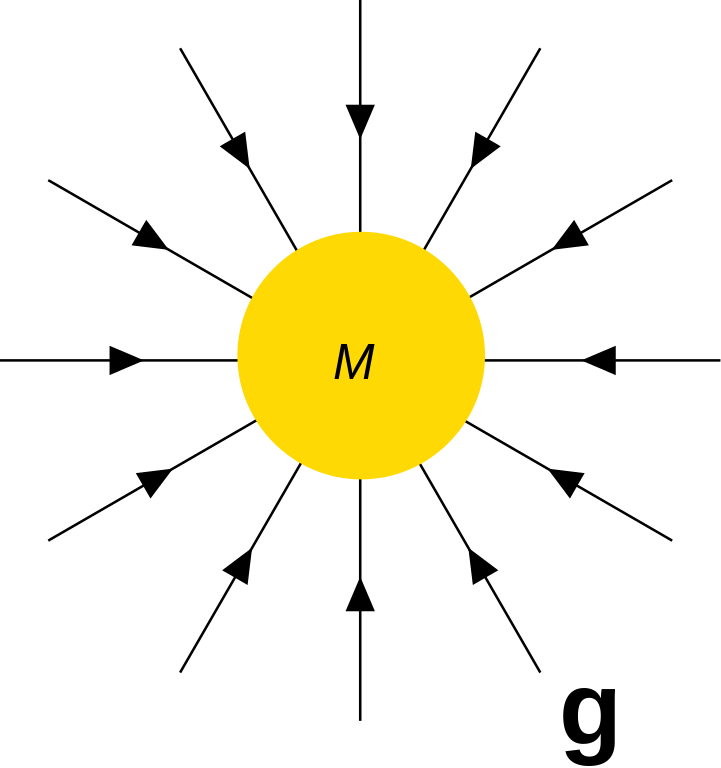
Physics - Classical Mechanics - Gravitational Fields

1.3 - Units and Standards - Physics LibreTexts PDF, PDF, International System Of Units

Physics, Definition, Types, Topics, Importance, & Facts
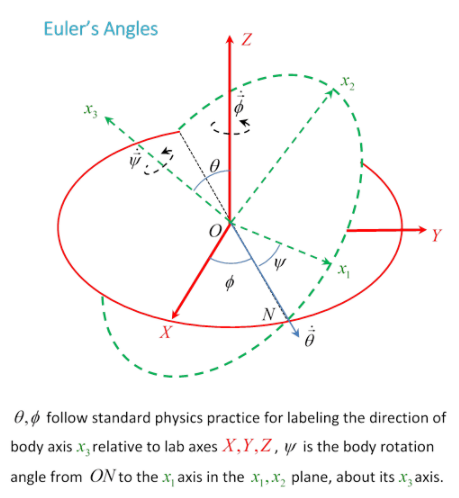
27.1: Definition of Euler Angles - Physics LibreTexts
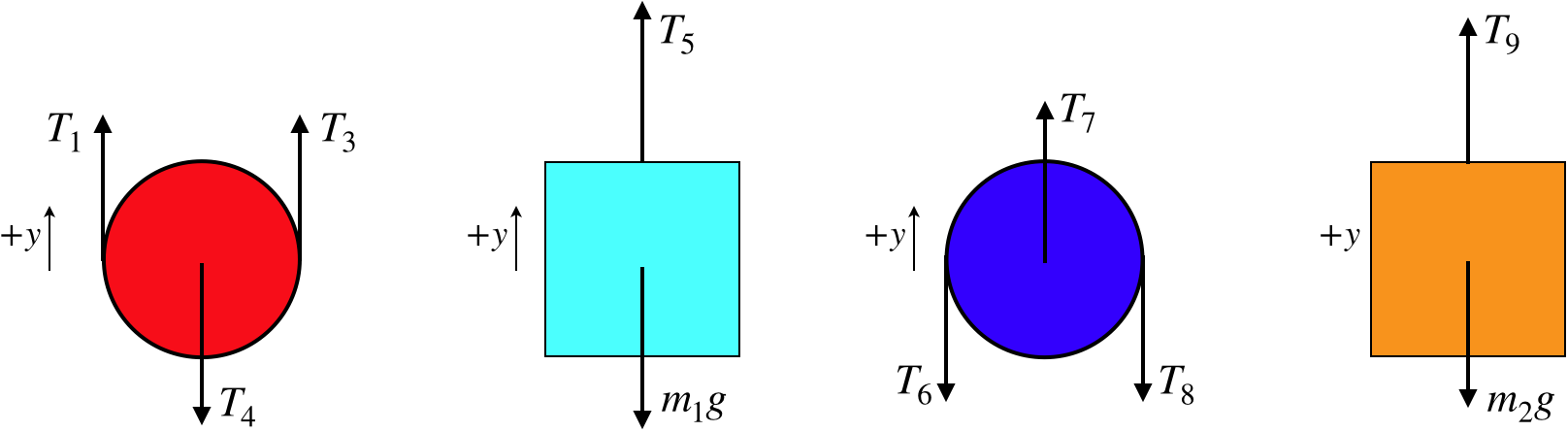
2.6: Additional Twists - Constraints - Physics LibreTexts
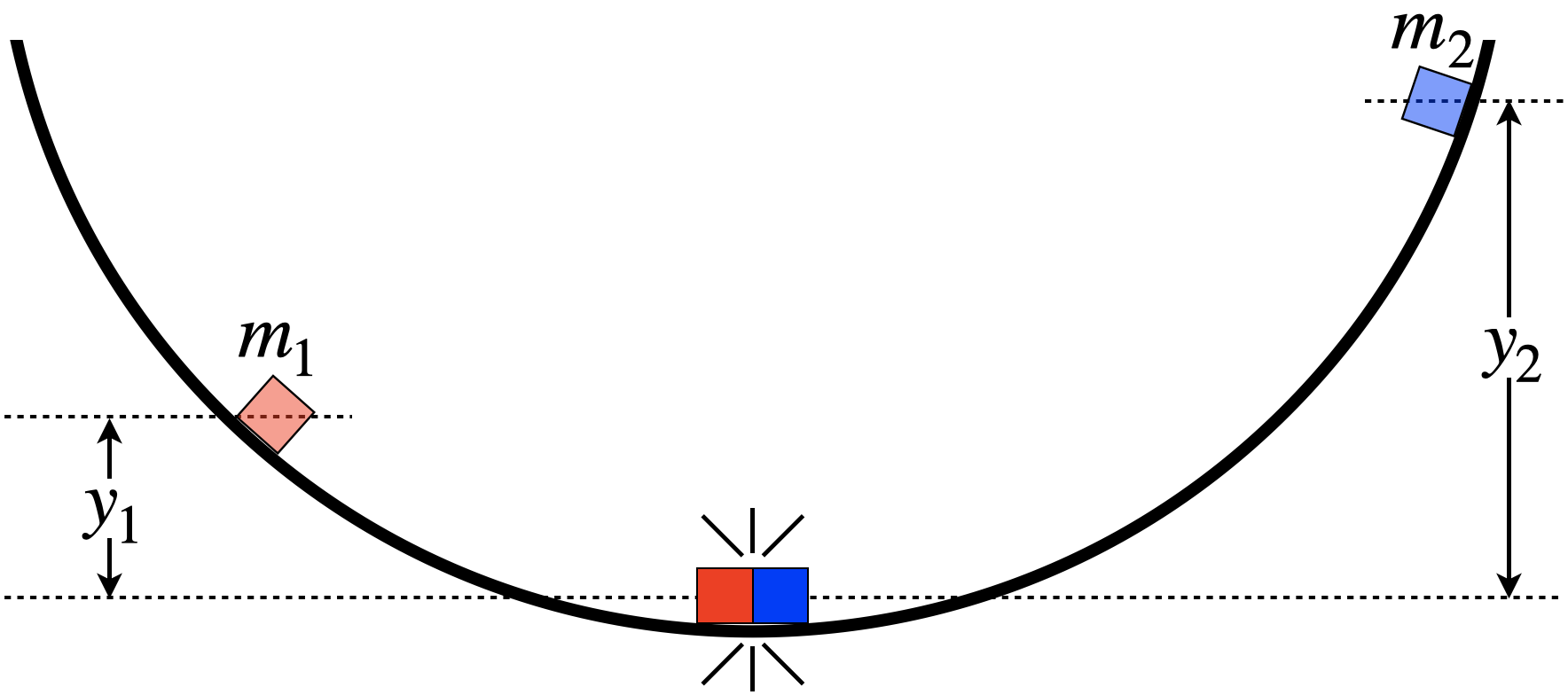
4.4: Momentum and Energy - Physics LibreTexts
- Dulce Maria chega ao Rio de Janeiro para shows do RBD no Brasil: 'estou muito feliz' - Zoeira - Diário do Nordeste

- Express Body Contour Stretch Cotton Square Neck Bodysuit Pink Women's L

- Conceito Do Amor E Dia De São Valentim, Cair Da Mensagem No Céu Ilustração do Vetor - Ilustração de decorativo, valentina: 104644994

- Proenza Stretch Satin Bralette Hangar9 Designer Fashion Canada

- Wholesale Strapless Silicone Bra, Wholesale Strapless Silicone Bra




