Inpatient Diabetes Guideline for Adult Non-Critically Ill Patients - NCBI Bookshelf

By A Mystery Man Writer
This guideline applies to hospitalized adult non-critically ill (non-ICU) patients in general medicine, surgical, perioperative, short-stay, and OB/GYN areas with Type 1 diabetes (T1DM), Type 2 diabetes (T2DM), stress hyperglycemia, diabetes secondary to medications, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. The objective is to promote safe, effective glycemic management in hospitalized patients targeting blood glucose (BG) to published goals while preventing hypoglycemia. Approximately 30–35% of admitted patients have diabetes. Hyperglycemia is a well-established risk factor for adverse hospital outcomes. Additionally, hypoglycemia can have deleterious consequences. Safe and effective glucose management is of paramount importance in the hospital. Additionally, a hospital admission is an opportune time to address diabetes control.
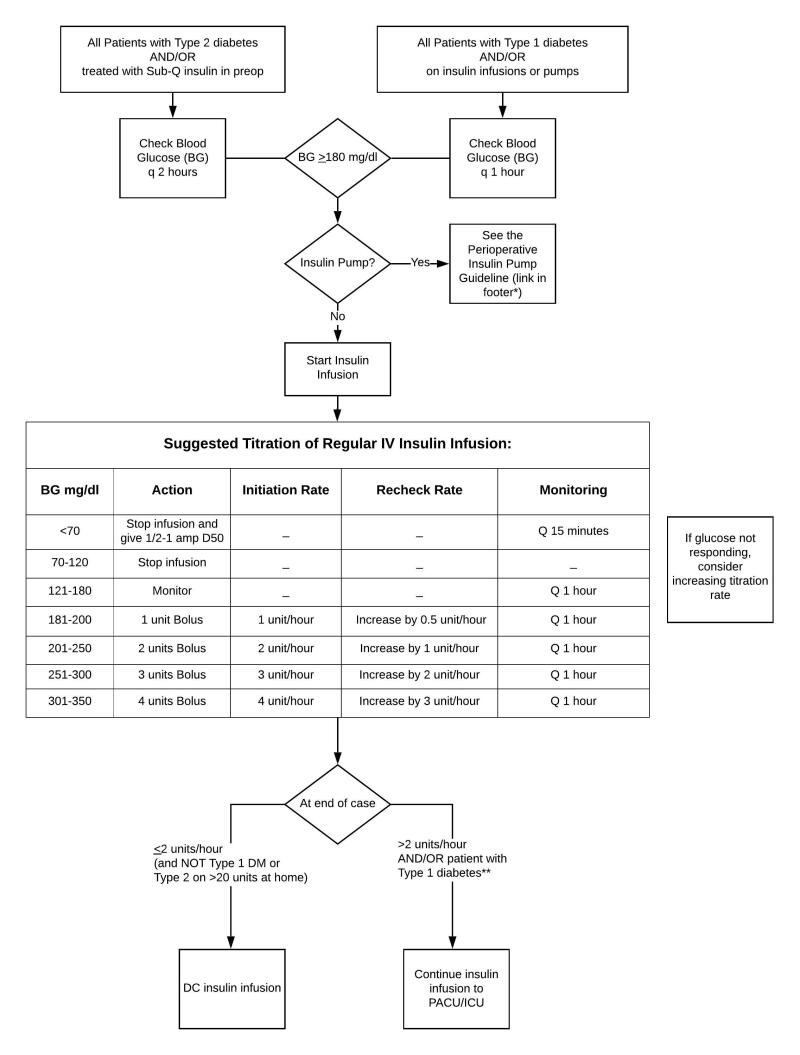
Inpatient Diabetes Guideline for Adult Non-Critically Ill Patients

References - Diabetes Medications for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes
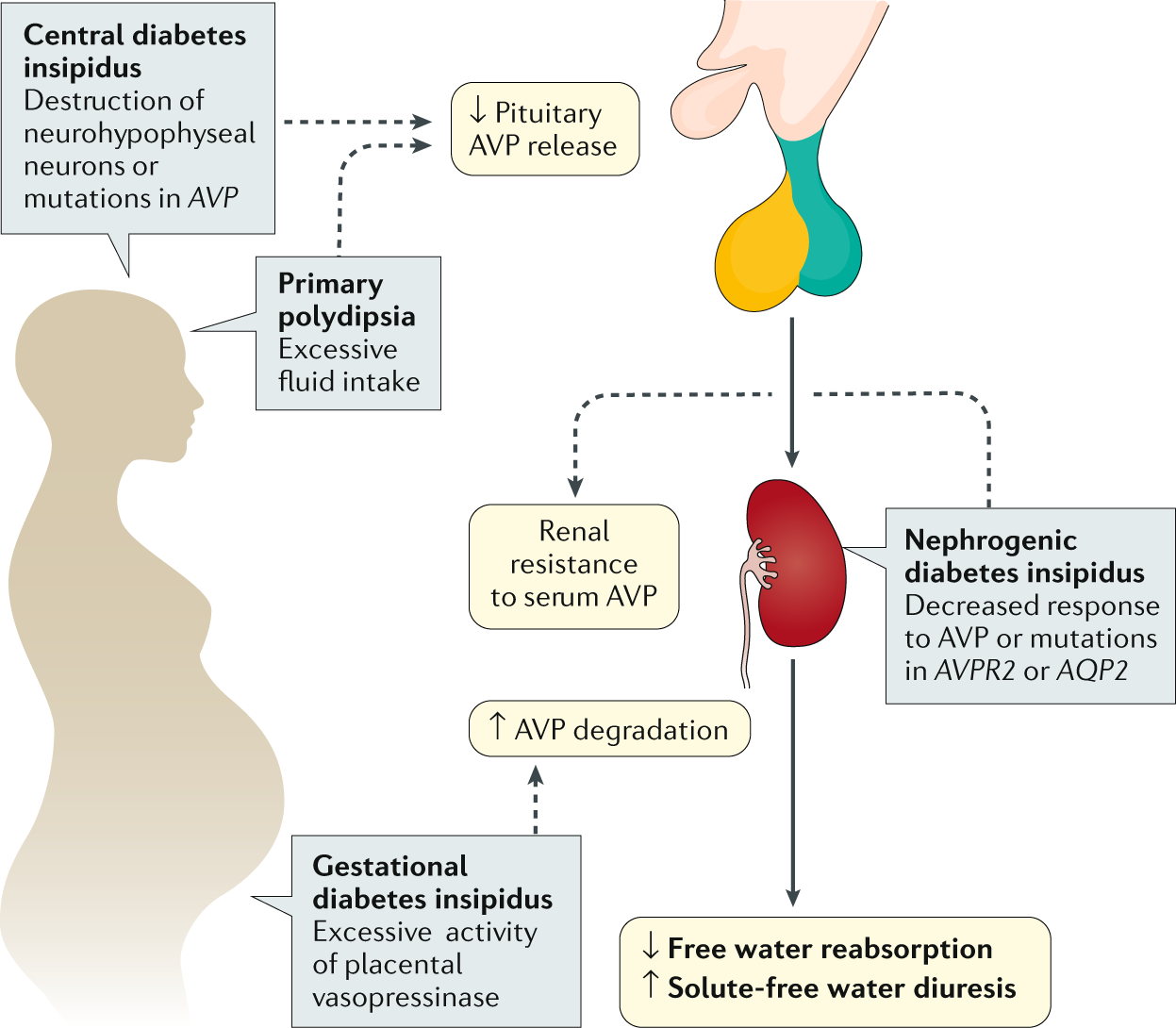
Diabetes insipidus Nature Reviews Disease Primers
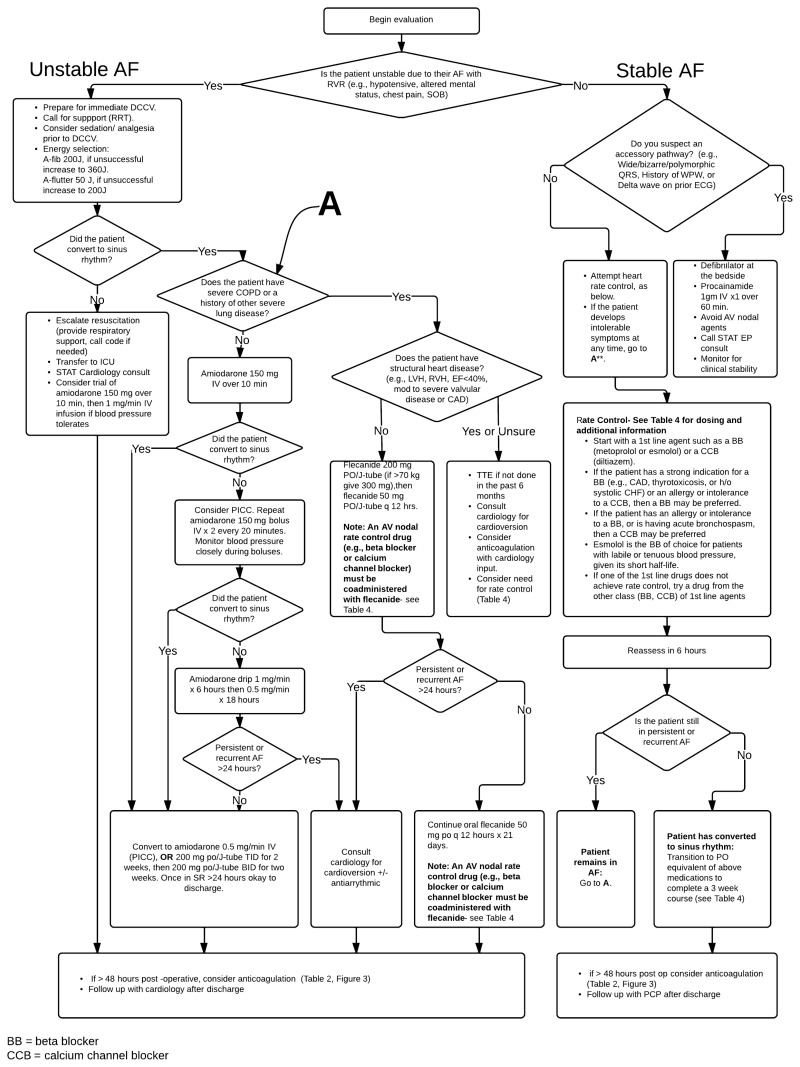
Inpatient Management of Acute Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial

2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A

Assessment of the patient with heart failure symptoms and risk

Diabetes Management in Hospitalized Patients: A Comprehensive

Hyperglycemic Crises: Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic

Poll Results: Deconditioning in Hospitalized Older Adults and the

The Management of Type 1 Diabetes - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Journal Club - Early versus Late Parenteral Nutrition in
- Fujian E-Time Electronic FZCO Products - Fujian E-Time Electronic

- NOVOLAN Lipstick & Lip Glosses 2 In 1 Liquid Lipstick, Velvet

- NOVOLAN Primer Foundation Makeup Egg 3 In 1 Makeup Kit, Liquid Foundation, Face Primer, Foundation Blending, Invisible Pore Primer Light Moisturizing Concealer Liquid Foundation Cosmetic Set 3Pcs price in Saudi Arabia

- Fujian E-Time Electronic FZCO Products - Fujian E-Time Electronic FZCO Store Online - Buy Fujian E-Time Electronic FZCO Products

- NOVOLAN Nursing Bra Maternity Bra, Pregnant Women's Front Buckle Large Size Nursing Underwear Thin Section Anti-Sagging Gathered Big Breasts Without Steel Ring Bra Nursing Clothes (S, Skin) : Buy Online at Best

- I-ILavento Women Y Back Sports Bra Spaghetti Straps Sri Lanka

- Americana Valmont dobra fábrica e usa força do sol para vender mais irrigação no Brasil - AgFeed

- JEANS BARBADOS PIERNA ANCHA TIRO ALTO

- It's finally here! 🎉 Introducing LipVelvet, a NEW, one-of-kind matte lip gloss, created in collaboration with @TaraThueson! . Together, we set out to, By Shine Cosmetics
- Buy Sona Lingerie Women's Non-Wired Bra (SLG-Perfecto-MRN-BLK-PNK-SKN_Maroon-Black-Pink-Skin_38) at

