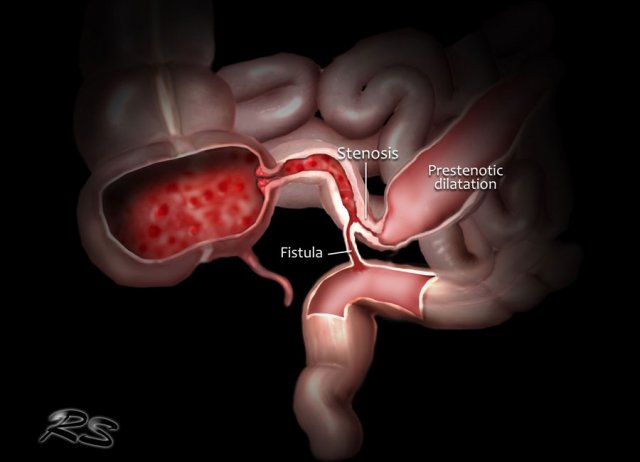
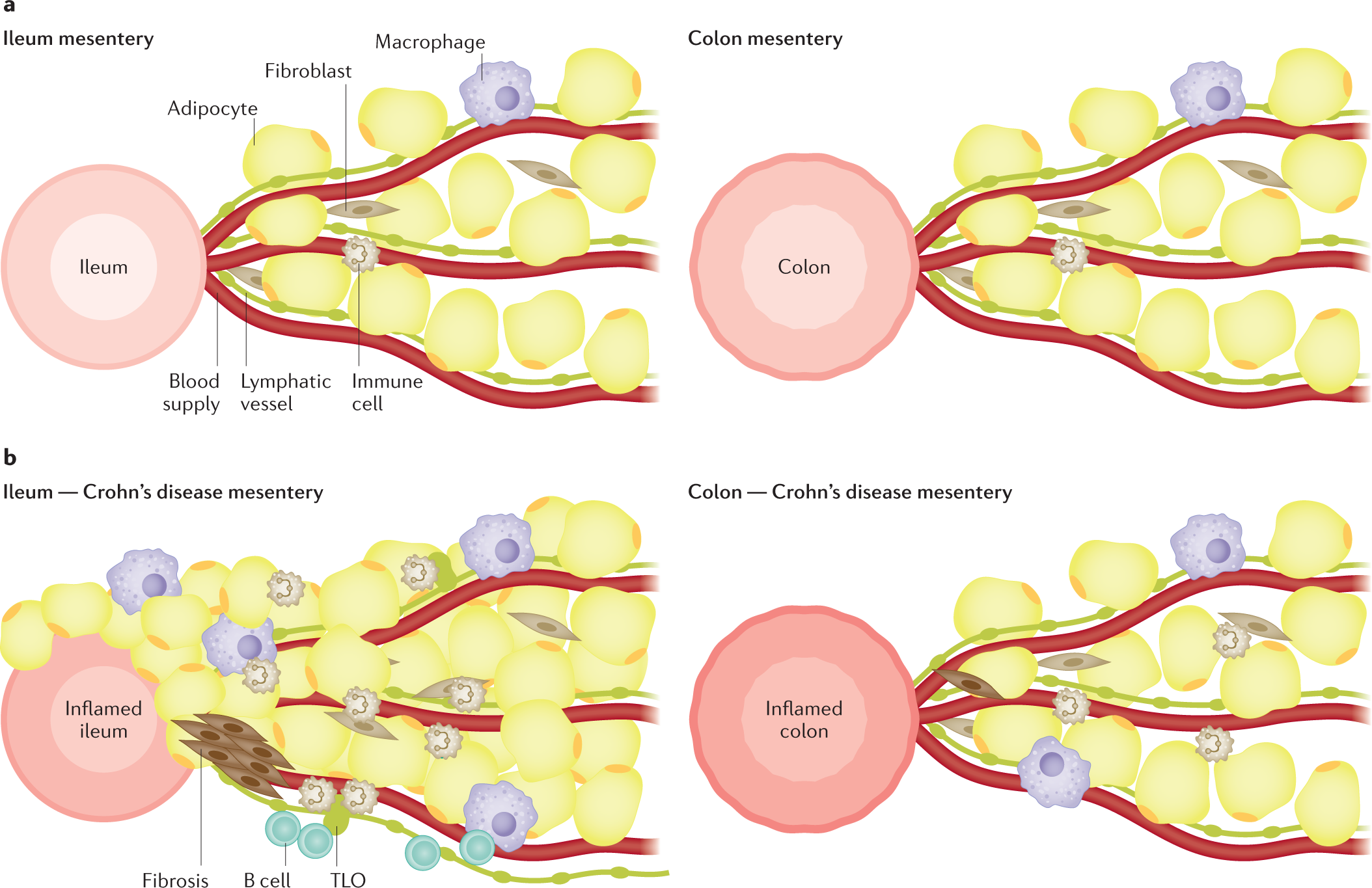
Location is important: differentiation between ileal and colonic Crohn's disease
By A Mystery Man Writer

Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children

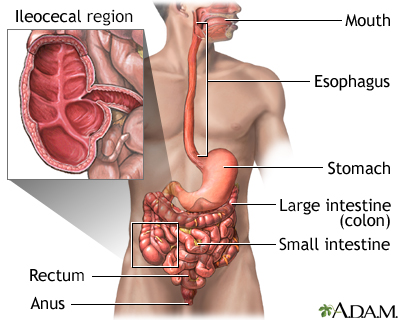
Crohn's disease
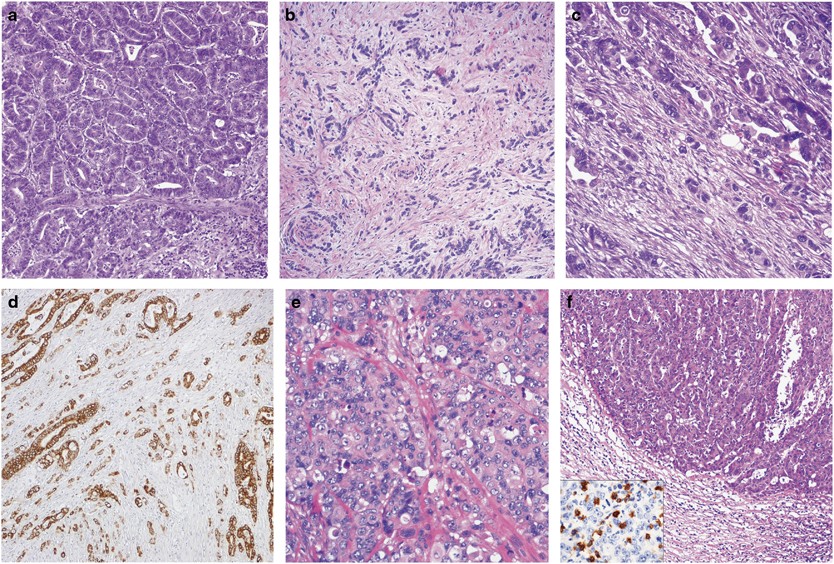
Small bowel carcinomas in celiac or Crohn's disease: distinctive histophenotypic, molecular and histogenetic patterns

Radiological biomarkers reflecting visceral fat distribution help distinguish inflammatory bowel disease subtypes: a multicenter cross-sectional study, Insights into Imaging
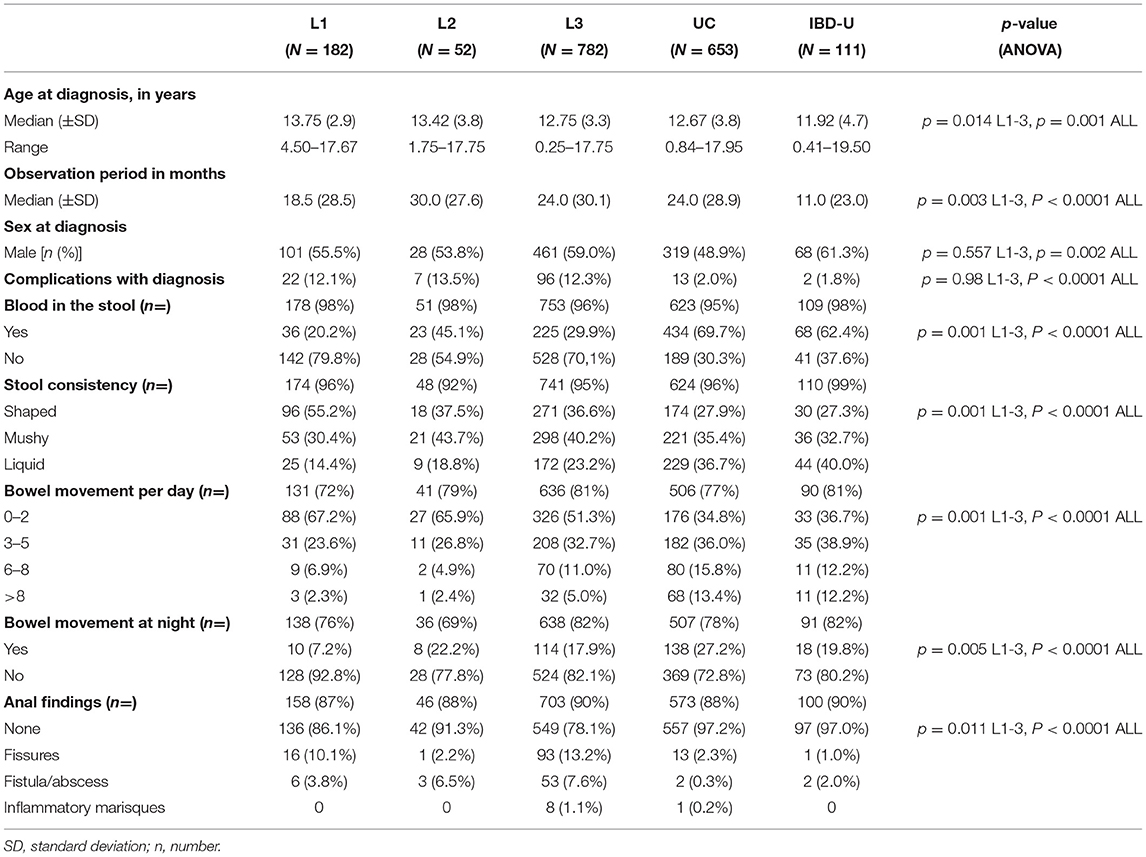
Frontiers Isolated Crohn's Colitis: Is Localization Crucial? Characteristics of Pediatric Patients From the CEDATA–GPGE Registry

PDF) Effects of visceral adipose tissue on anti-tumour necrosis factor-α in Crohn's disease

Altered Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics in Crohn's Disease: Capturing Systems Parameters for PBPK to Assist with Predicting the Fate of Orally Administered Drugs

Pro-inflammatory innate-like T cells are expanded in the blood and
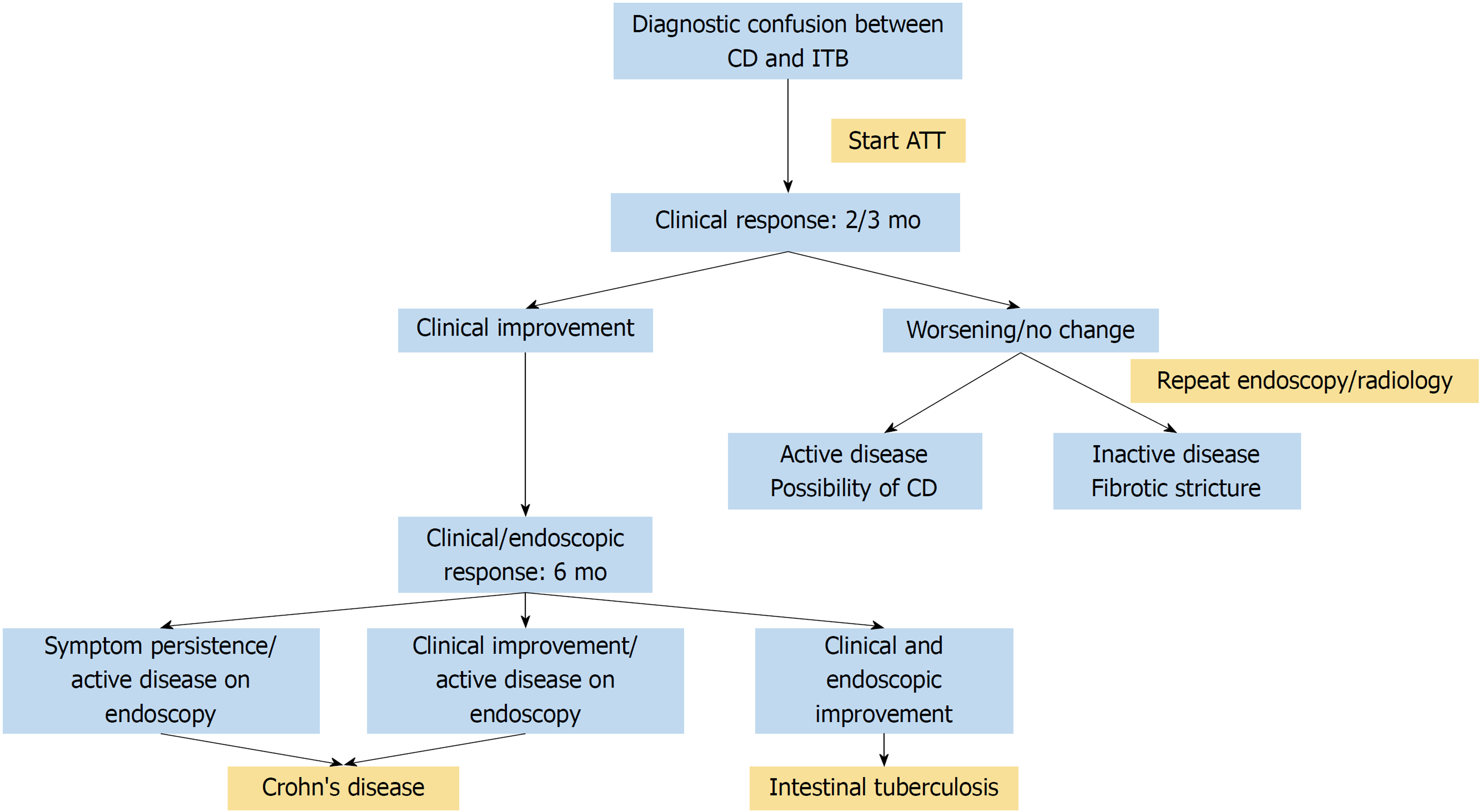
Differentiating Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis

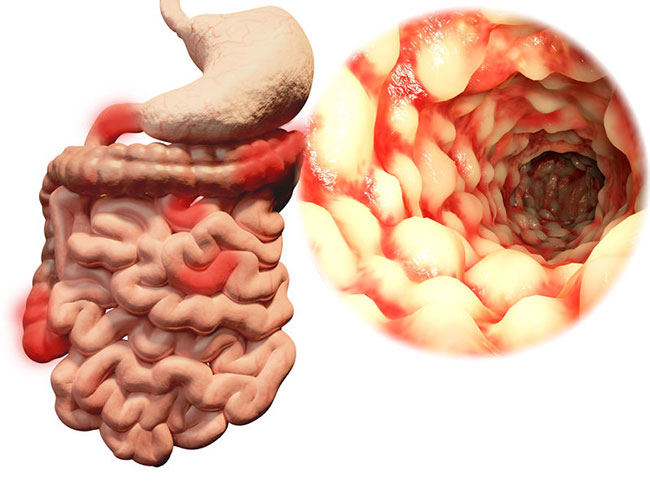
Frontiers Crohn's disease patients with L4-esophagogastroduodenal phenotype is associated with a better prognosis: A retrospective cohort study

Ileal mucus viscoelastic properties differ in Crohn's disease

Cigarette smoking and CD location according to the Montreal Classification.

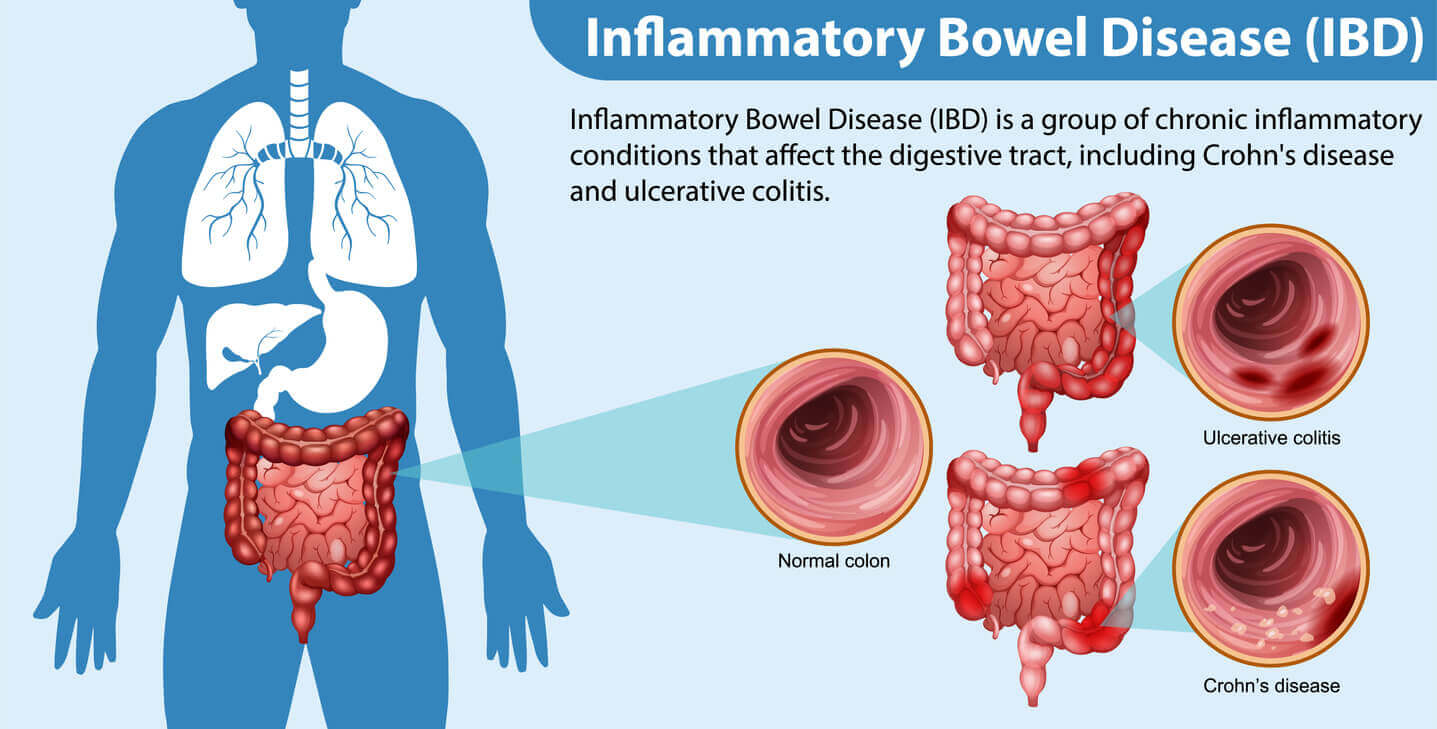
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
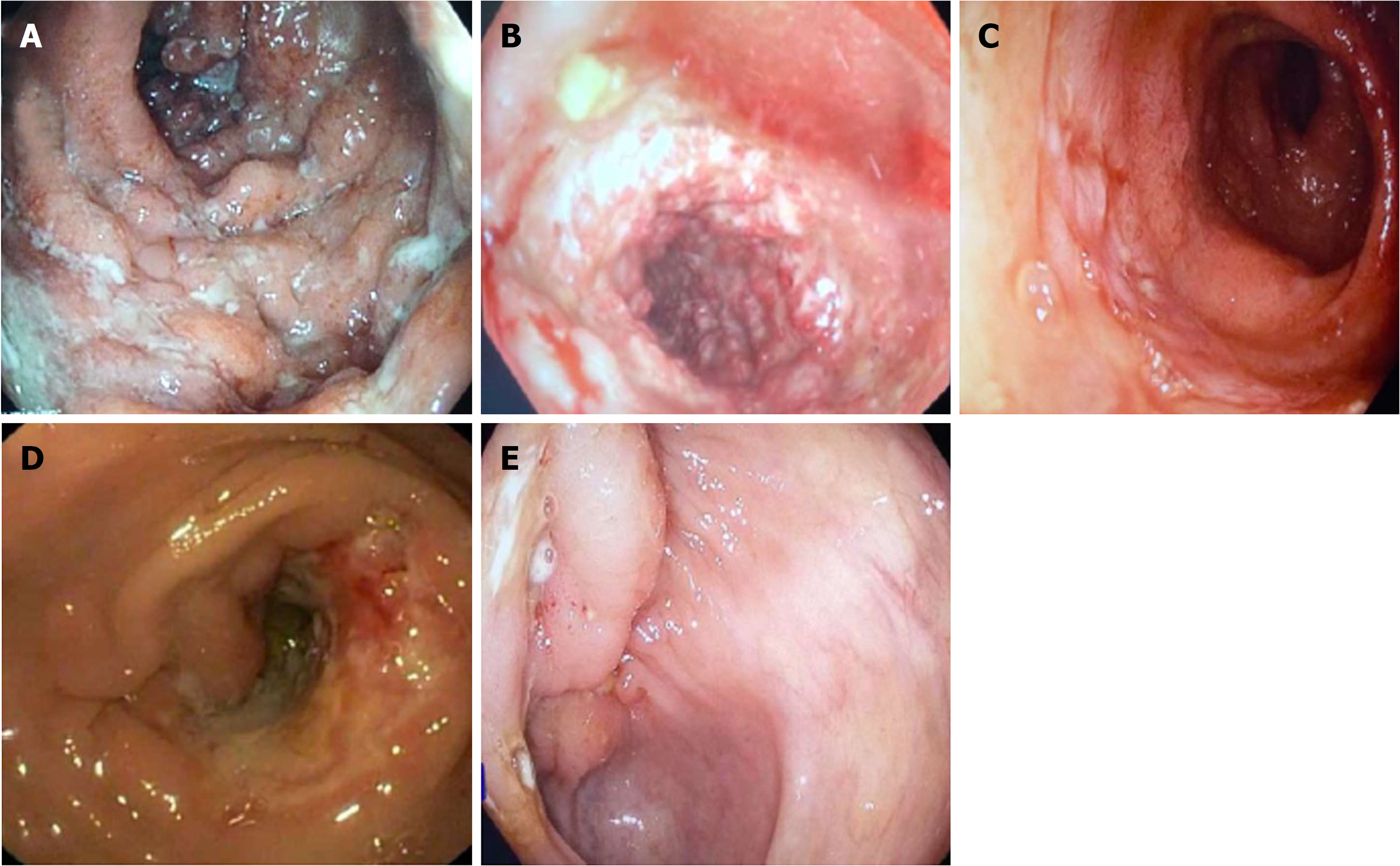
Differentiating Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/risks-of-untreated-crohn-s-disease-4707022_FINAL-0c4c4c50d40441399a7089d4d23ab812.png)